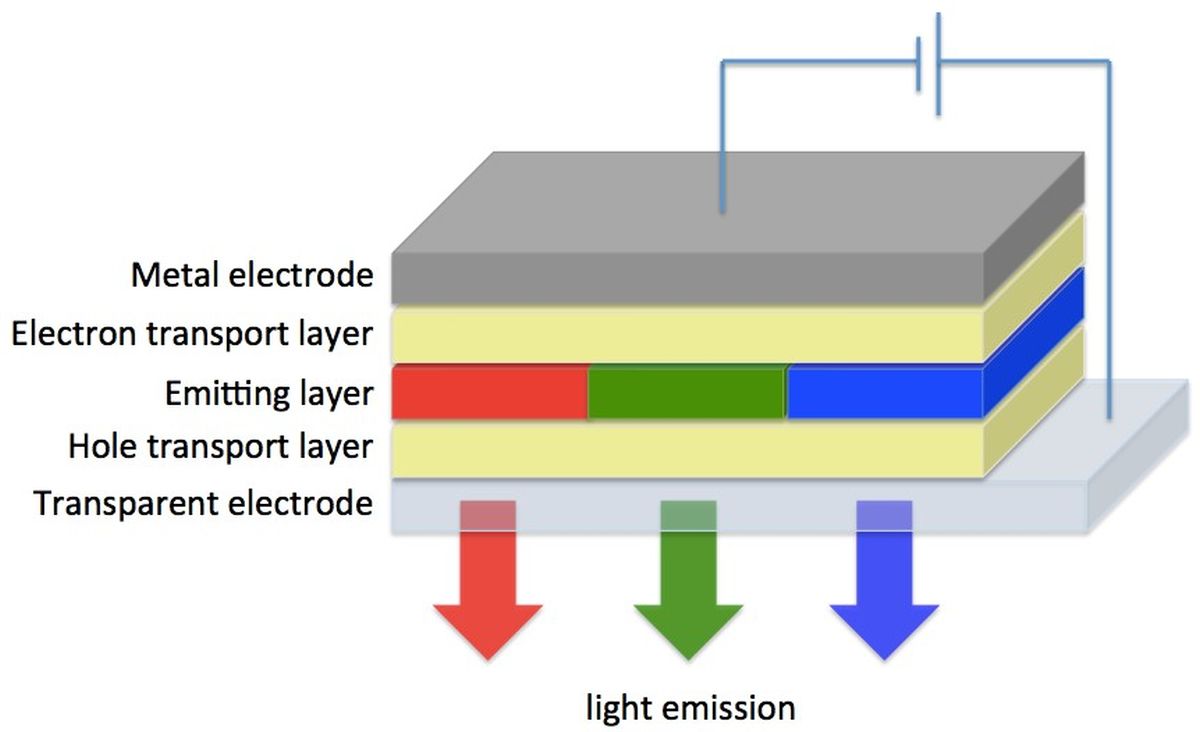
Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED): The Next-Generation Display Technology
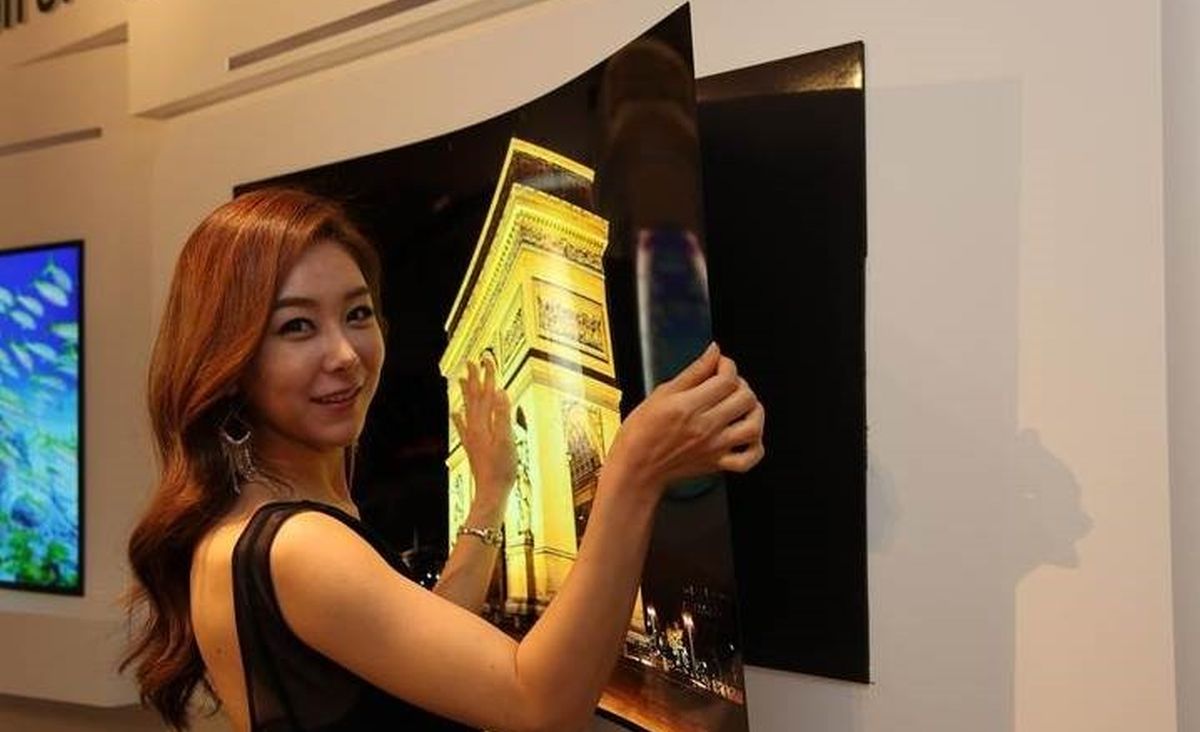
Imagine a large flat-screen TV that can be pasted onto a wall like a piece of wallpaper. This was once a futuristic concept but is fast becoming a practical reality. A flexible 55” OLED TV with a thickness that measures only 0.97mm has recently been showcased in the market. This TV is so thin and light that it can be mounted on any surface with hardly any effort like sticking a strip of magnetic pad on a refrigerator. OLED, which stands for organic light emitting diode, was first invented by IAS Bank of East Asia Professor Ching W. TANG some 30 years ago when he was working at the Kodak Research Laboratories. Today, OLED displays can be found in a wide range of consumer products, including smartphones, tablets, TVs,and trendier wearable electronics. Widely acclaimed because of its many differentiating features, OLED is gaining ground in the display industry with the potential to be the next-generation display technology.